Glaucoma Treatment
The Evista Eye Centre offers comprehensive Glaucoma care and consultations for all forms of Glaucoma. We care for infants and children, adults, whether primary or related to complex eye problems. Medical treatment, Laser therapies, and Surgical procedures for Glaucoma are available at Evista Eye Care Centre.
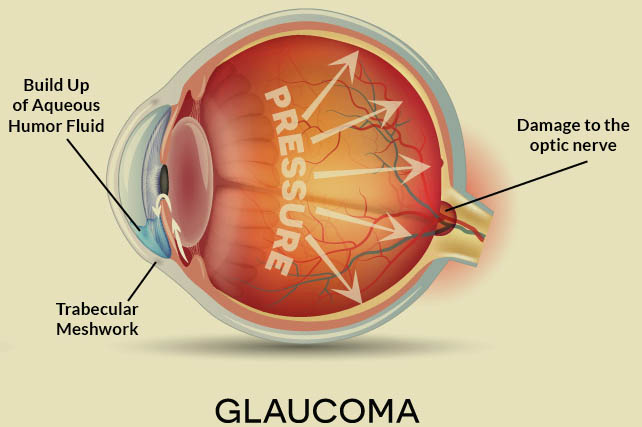
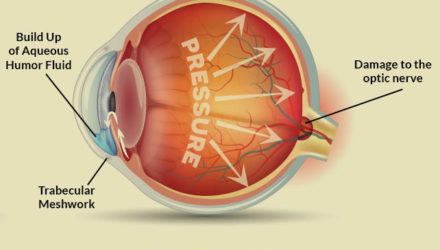
Glaucoma is a group of diseases that damage the eye’s Optic nerve and can result in vision loss and blindness.
However, with early detection and treatment, you can often protect your eyes against serious vision loss.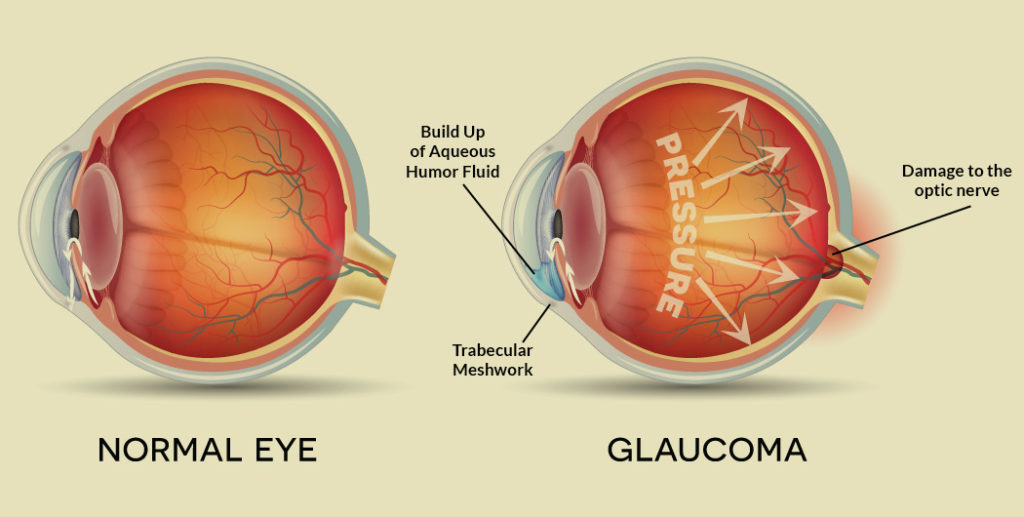
The Optic Nerve
The optic nerve is a bundle of more than 1 million nerve fibers. It connects the Retina to the brain. (See diagram above.) The Retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. A healthy Optic nerve is necessary for good vision.
Glaucoma Symptoms
At first, Open-angle Glaucoma has no symptoms. It causes no pain. Vision stays normal. Glaucoma can develop in one or both eyes.
Without treatment, people with Glaucoma will slowly lose their Peripheral (side) vision. As Glaucoma remains untreated, people may miss objects to the side and out of the corner of their eye. They seem to be looking through a tunnel. Over time, straight-ahead (central) vision may decrease until no vision remains.
Glaucoma is detected through a comprehensive dilated eye exam that includes the following:
Visual acuity test. This eye chart test measures how well you see at various distances.
Visual field test. This test measures your Peripheral (side vision). It helps your eye care professional to tell if you have lost peripheral vision, a sign of Glaucoma.
Dilated eye exam. In this exam, drops are placed in your eyes to widen, or dilate, the pupils. Your eye care professional uses a special magnifying lens to examine your retina and Optic nerve for signs of damage and other eye problems. After the exam, your close-up vision may remain blurred for several hours.
Tonometry is the measurement of pressure inside the eye by using an instrument called a Tonometer. Numbing drops may be applied to your eye for this test. A Tonometer measures pressure inside the eye to detect Glaucoma.
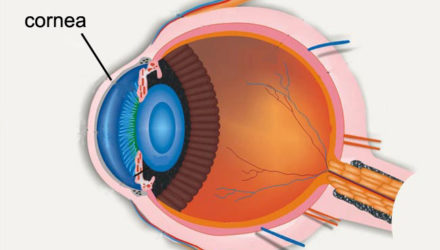
Pachymetry is the measurement of the thickness of your cornea. Your eye care professional applies a numbing drop to your eye and uses an ultrasonic wave instrument to measure the thickness of your cornea.
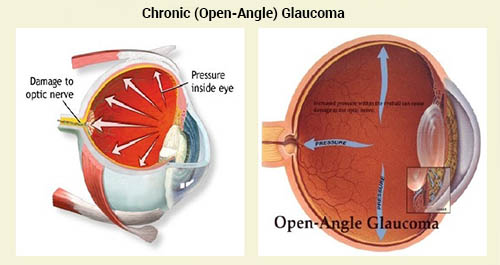 Chronic Open Angle Glaucoma: The most common type of glaucoma, known as chronic open angle (COAG) or primary open angle, occurs when the canals draining the eye of aqueous humor become clogged.
Chronic Open Angle Glaucoma: The most common type of glaucoma, known as chronic open angle (COAG) or primary open angle, occurs when the canals draining the eye of aqueous humor become clogged.This blockage can gradually increase pressure within the eye to damaging levels. No pain occurs, so individuals are usually unaware that these changes are occurring.
There are no early signs or symptoms but over the years vision will be lost starting in the Periphery and moving towards the central vision.
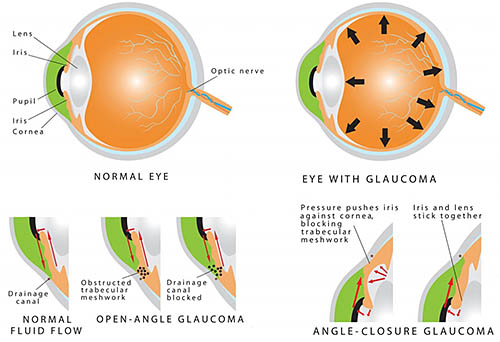
Acute Angle Closure Glaucoma: When eye pressure builds up rapidly, it is called Acute angle-closure Glaucoma. This type of glaucoma commonly occurs in individuals who have narrow anterior chamber angles.
In these cases, aqueous fluid behind the iris cannot pass through the pupil thus pushing the iris forward, preventing aqueous drainage through the angle.
It is as though a sheet of paper floating near a drain suddenly drops over the opening and blocks the flow out of the sink. In cases of Acute angle closure Glaucoma, one may experience blurred vision, halos around lights, deep pain behind the eye, nausea, and vomiting.